Microscopic Revolution under Shadowless Light: Five Types of Surgical Microscopes Reshaping Modern Surgery
From repairing cerebral aneurysms in neurosurgery to treating root canals in dental pulp, from suturing 0.2mm blood vessels to precise manipulation of inner ear mazes, surgical microscopes have become an irreplaceable "second pair of eyes" in modern medicine.
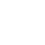
In the operating room of Yantai Yeda Hospital, orthopedic doctors are performing a finger replantation surgery. They picked up a blood vessel with a diameter of only 0.2 millimeters with tweezers in their hands and threaded the needle under the operating microscope like embroidery. At the same time, in the operating room of the Federal University of S ã o Paulo in Brazil, neurosurgeons can clearly distinguish the boundary between arachnoid cysts and surrounding brain tissue through the eyepiece of a Neurosurgery microscope.
Surgical microscopes have evolved from simple magnifying tools to precision systems that integrate optical imaging, fluorescence navigation, augmented reality, and other technologies, becoming the "second pair of eyes" in surgical procedures.
01 Neurosurgical surgical microscope, precise navigation of deep cavities
Neurosurgery microscopes can be regarded as the jewel in the crown of microsurgery, and their technical complexity represents the highest level in the industry. In the field of neurosurgery, neurosurgical microscopes need to be operated in deep and narrow cranial cavities while avoiding important functional anatomical structures.
The CORDER ASOM-630 series operating microscope integrates three core technologies: augmented reality fluorescence technology can display blood flow in real-time during cerebrovascular surgery; Fusion Optics technology provides greater depth of field; The high-definition optical system projects images to the surgeon's field of view, achieving the precision requirements of microsurgery. In a Galassi III arachnoid cyst surgery, the ASOM-630 neurosurgical microscope clearly demonstrated the complex relationship between the cyst wall and surrounding blood vessels and nerves, allowing doctors to accurately separate without damaging critical structures.
In cerebrovascular surgery, fluorescence technology combines indocyanine green fluorescence with natural tissue images in real-time. Doctors can simultaneously observe the morphology and hemodynamics of aneurysms without switching between black and white fluorescence modes, greatly improving surgical safety.
02 Dental surgical microscope, a microscopic revolution within the root canal
In the field of dentistry, the application of dental operating microscopes has led to a qualitative leap in treatment accuracy. These dental microscopes increase the magnification to over 20 times, combined with high-resolution imaging systems, ushering dental pulp treatment into the 'microscopic era'.
The core challenge of dental microscopes lies in balancing optical accuracy with ergonomic design. The technical engineers of Chengdu CORDER Optics&Electronics Co., Ltd. are known for their "sharp eyes", and their calibrated binocular optical path deviation is strictly controlled within 0.2 millimeters. Beyond this threshold, doctors will experience disparity conflicts between their eyes, leading to visual fatigue, "explained technical supervisor Zhu.
In root canal treatment, doctors can clearly observe complex anatomy such as the root canal isthmus and lateral branch root canals, significantly reducing the probability of missing infected lesions. The latest research shows that using a dental operating microscope for operation significantly improves the accuracy of fiber post extraction. Although the operation time has slightly increased, it has important value in preserving healthy dental tissue.
03 ENT Microscope, Cold Light Sharp Blade for Deep Chamber Surgery
The otolaryngology surgical microscope is designed to handle the complex canal structure from the tympanic cavity to the glottis. Modern otolaryngology microscopes have six degrees of freedom of movement, The primary and secondary observation mirrors can achieve synchronous observation at the same magnification, field of view, and orientation. Its optical hinged tube can tilt 0-90 degrees, allowing doctors to maintain a comfortable position.
High brightness coaxial illumination combined with a 1:5 electric continuous zoom system can clearly display the fine structure of the ossicular chain during tympanoplasty. The cold light source illumination system provides over 100000LX field illumination without damaging sensitive inner ear structures due to heat.
04 Orthopedic surgical microscope, millimeter level vascular suturing art
Orthopedic operating microscopes are creating a miracle of life in the field of limb replantation and reconstruction. The bone department team of Yantai Yeda Hospital completes multiple finger replantation surgeries every week, and their "embroidery skills" are based on precise microscopic equipment.
In typical distal finger replantation, doctors face the challenge of vascular anastomosis with a diameter of only 0.2 millimeters, which is equivalent to the fine structure of hair strands. Under the Orthopedic microscope, doctors can clearly distinguish the condition of the vascular endothelium and determine whether to remove the damaged segment to avoid postoperative thrombosis. If there is a deviation in the optical path, it is equivalent to the left eye being normal and the right eye being elevated. Over time, the eyes will become very tired, "said a senior microscopy expert describing the importance of calibration accuracy.
The department also performs high difficulty surgeries such as perforator flap transplantation, and applies microsurgical techniques to repair composite tissue defects in the limbs. They use the technique of free skin flap that anastomoses blood vessels to precisely connect the skin flap with the tiny blood vessels in the recipient area under a operating microscope.
---
With the deep integration of augmented reality (AR) technology and operating microscopes, neurosurgeons can now directly "see" navigation markers and fluorescent blood flow in the natural depth of field of brain tissue. In the dental clinic, 4K ultra high definition images are projected onto a large screen through low latency transmission technology, allowing the entire medical team to share a microscopic view.
In the future operating room, a surgeon may use an orthopedic surgical microscope to complete a "life embroidery" of 0.2mm blood vessels in the morning, and then transfer to the neurosurgery operating room in the afternoon to clamp a cerebral aneurysm under augmented reality fluorescence guidance.
Surgery Microscopes will continuously break through the visual field limitations of deep cavity surgeries, illuminating the most secretive corners of the human body with clearer optical techniques.
Post time: May-29-2025