Innovations in Surgical Microscopy: Enhancing Precision Across Medical Disciplines
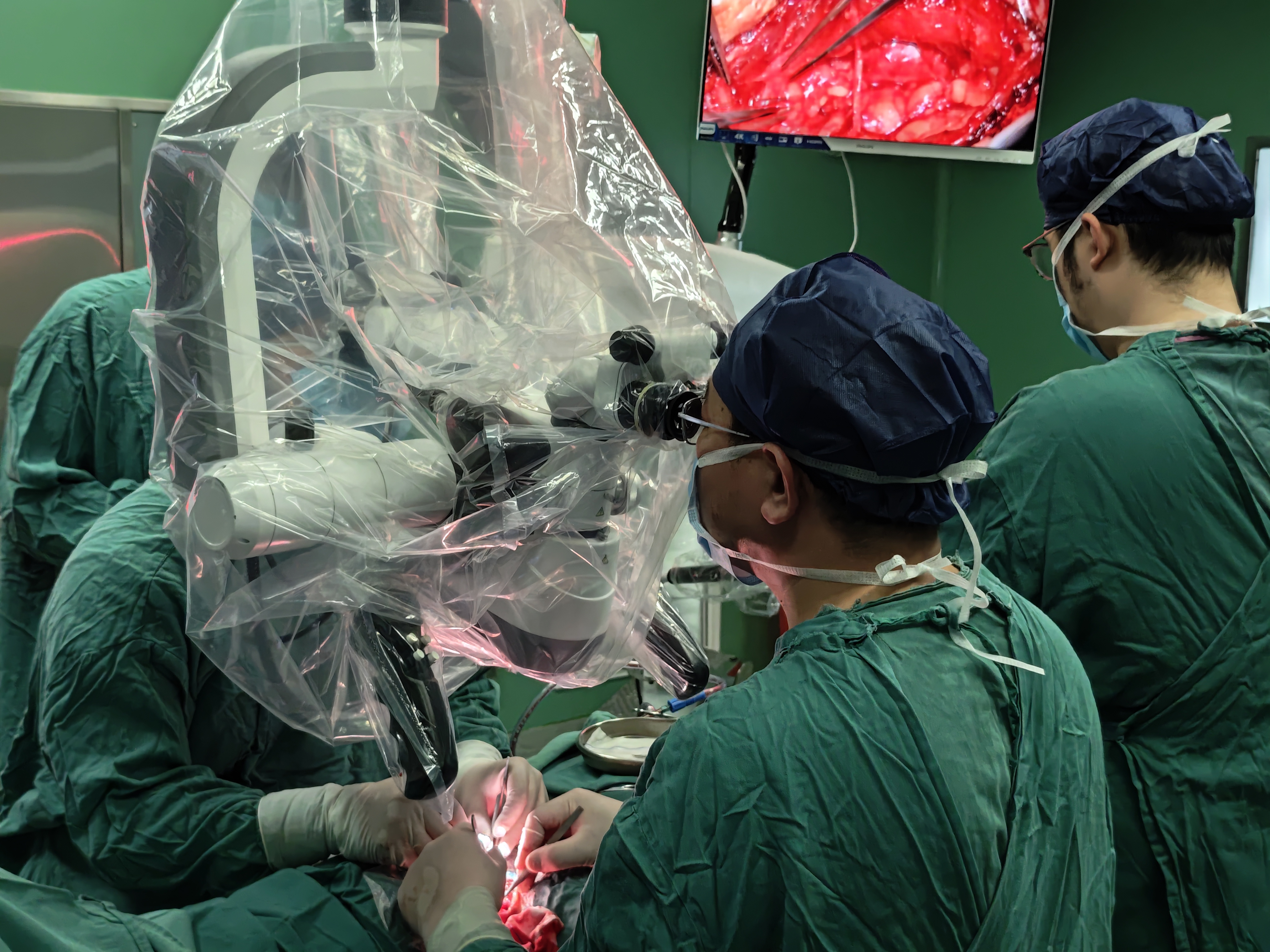
The field of surgical microscopy has undergone transformative advancements, driven by the demand for precision, versatility, and adaptability in modern medical procedures. From delicate spinal cord microscope applications to specialized tools like the ENT microscope-inspired optical systems, these devices have become indispensable across diverse specialties, including orthopedics, ophthalmology, and traumatology. This article explores the evolving landscape of medical microscopes, emphasizing their critical role in improving patient outcomes and expanding surgical possibilities.
At the core of neurosurgery and complex spinal interventions lies the spinal cord microscope, a pinnacle of engineering designed to illuminate and magnify intricate neural structures. Similarly, spine microscope systems cater to procedures requiring sub-millimeter accuracy, such as decompression or fusion surgeries. These tools often integrate with binocular microscope configurations, providing surgeons with stereoscopic vision essential for depth perception in confined anatomical spaces. Parallel innovations are evident in ENT (ear, nose, and throat) surgery, where high-resolution ENT microscope systems enable precise visualization of sinus pathways and vocal cord structures.
Ophthalmic surgery has similarly benefited from advancements in ophthalmic surgical products, particularly ocular microscope systems tailored for retinal repairs and cataract removal. These devices often feature modular designs, allowing seamless integration with led lamp surgical microscope components to enhance illumination without thermal interference. Meanwhile, the photo colposcopes market reflects growing demand for imaging solutions in gynecological diagnostics, combining magnification with digital capture capabilities for accurate lesion assessment.
Dentistry, too, has embraced microsurgical techniques, with dental operating microscope systems revolutionizing endodontics and periodontal surgeries. The availability of customizable dental microscope parts, such as ergonomic eyepieces and adjustable focal lengths, ensures adaptability across procedures. Furthermore, face to face surgical microscope setups improve collaboration between surgeons and assistants during complex dental restorations.
Orthopedic and traumatology applications rely heavily on orthopedic operating microscope and traumatology operating microscope systems, which facilitate the repair of fractures, ligament reconstructions, and joint revisions. These specialties demand rugged yet precise tools, often incorporating handle control microscope mechanisms for intraoperative adjustments. In vascular surgery, vascular operating microscope and vascular suture microscope technologies have redefined anastomosis procedures, enabling surgeons to work with vessels as fine as 0.3 mm in diameter.
The shift toward minimally invasive techniques has spurred demand for portable operating microscope units, which combine compact designs with high-performance optics. These systems are particularly valuable in field hospitals or multi-room clinics. Conversely, mounted-wall operation microscope installations remain popular in dedicated operating theaters, offering stability and reduced footprint. Hybrid solutions like multifunctional operating microscope platforms further bridge this gap, providing modular attachments for specialties ranging from plastic surgery (plastic surgery microscope) to vascular interventions.
Technological integration plays a pivotal role in modern surgical microscope development. Innovations such as led lamp surgical microscope components not only improve energy efficiency but also reduce heat emission, minimizing tissue desiccation during prolonged procedures. Ergonomics have also been prioritized, with adjustable handle control microscope interfaces and customizable ocular arrangements reducing surgeon fatigue. The term microscopio, often used interchangeably in global medical contexts, underscores the universal reliance on these devices across linguistic and regional boundaries.
Economic factors, such as colposcopy price trends and reimbursement policies, influence adoption rates in diagnostic fields. However, the long-term cost-effectiveness of advanced medical microscopes lies in their ability to reduce procedural complications and recovery times. For instance, plastic surgery microscope systems enhance the precision of flap surgeries and microvascular repairs, directly impacting aesthetic outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the convergence of imaging technologies and artificial intelligence promises to further elevate medical surgical microscopes into smart diagnostic tools. Real-time image analysis, 3D mapping, and augmented reality overlays are poised to integrate with platforms like the binocular operating microscope, transforming passive visualization into interactive guidance systems. Such advancements will solidify the role of surgical microscope innovations as cornerstones of modern operative care, ensuring that specialties from neurosurgery to dermatology continue to achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy and safety.
In conclusion, the surgical microscopy industry exemplifies the synergy between engineering excellence and clinical necessity. Whether through the refined optics of an ocular microscope or the rugged versatility of a traumatology operating microscope, these devices collectively underscore a singular truth: in the quest to heal, clarity of vision remains as vital as the skill of the hand holding the scalpel.
Post time: May-12-2025